Féléves feladat
|
Söntellenállás vizsgálata | ||
|
Oktató
|
További oktatók:
| |
A feladat célja
A hallgatók elsajátítsák az elektromágneses térszámítás alapjait, főbb lépéseit, valamint gyakorlatot szerezzen az eredmények kiértékelésében és a nemzetközi elvárásoknak megfelelő Műszaki Jelentés (Technical Report) írásában.
A feladat megoldásához szükséges ismeretek
- A végeselem-módszer lépései;
- Az áramvezetési feladatra vonatkozó elméleti ismeretek (anyagok definiálásához, gerjesztés megadásához);
- A geometria elkészítéséhez CAD rendszer ismerete;
- Az Ansys Electronics Desktop Student letöltése és telepítése.
A féléves feladat
A feladat két részből áll, egy alapfeladatból, amely hibátlan megoldásával maximum 80%, és egy plusz feladatból, amivel további maximum 20% érhető el.
Leadási határidő: Lásd a feladatkiírásnál! Leadás formája: PDF formátumban. A színes ábrákat úgy kell elkészíteni, hogy fekete-fehérben kinyomtatva is világos legyen a tartalmuk az olvasó számára. Benyújtás nyelve: Magyar Benyújtás helye: A Moodle rendszerben kiírt feladatnál. Késői benyújtás: Minden megkezdett nap után 5% levonás az elért eredményből (azaz pl. 5 nap késés után 100%-os leadandóra már csak max. 100% - 5x5% = 75%-ot lehet szerezni). Értékelés: 0 – 50% - Elégtelen (1) 51 – 60% - Elégséges (2) 61 – 70% - Közepes (3) 71 – 85% - Jó (4) 86 – 100% - Jeles (5) A formai követelmények tekintetében itt is az áramlástan és a mechanika résznél megismert elvárások érvényesek.
Feladat I. része
Calculating the resistance and the total loss of the shunt resistor by finite element method
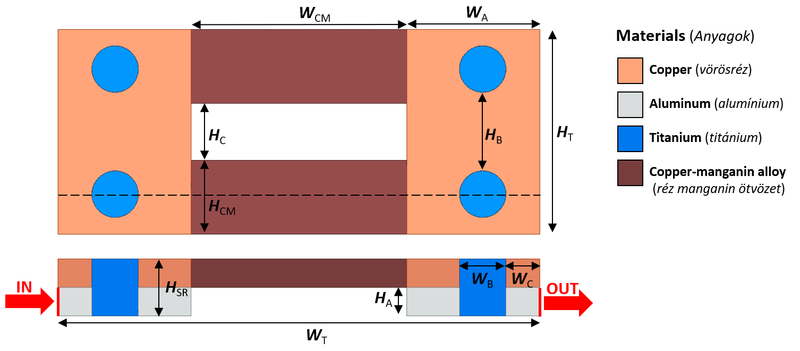
The geometry dimensions for your task you can find in the following table: Semester Assigment.
This task is a DC current conduction problem. The solved equation is
[math]\nabla\cdot\sigma\nabla \varphi=0[/math]
with following boundary conditions
[math]\vec{J}\cdot\vec{n}=-J_{\text{n}}[/math] on [math]\Gamma_{\text{J}}[/math] (This is the input)
and
[math]\varphi=U_0 = \text{0 V}[/math] on [math]\Gamma_{\text{E}}[/math] (This is the output),
where [math]J_{\text{n}}[/math] is the current density calculated from the specified current excitation.
The task: determine the voltage drop, the resistance and the ohmic loss of the problem.
The voltage drop is the potential difference between the two terminals of the arrangement. You can determine resistance using Ohm's law:[math]R = \frac{U}{I}[/math],
then the ohmic loss
[math]P = I^2\cdot R[/math]
where [math]U[/math] is the voltage drop, [math]I[/math] is the current and [math]R[/math] is the resistance.
Bulk conductivity of materials. Material Titanium Copper Aluminum Copper-manganin alloy [math]\sigma~[\text{MS/m}][/math] 1.82 58 38 20.833 Tasks
- Draw the geometry based on the specified dimensions.
- Define the problem based on the given material parameters and boundary conditions;
- Creating and specifying the task geometry in Ansys Electronics Desktop Student;
- Run the FEM simulation;
The parameters listed in the task can be calculated with the Maxwell 3D - DC Conduction solver and the Q3D Extractor - DC solver.
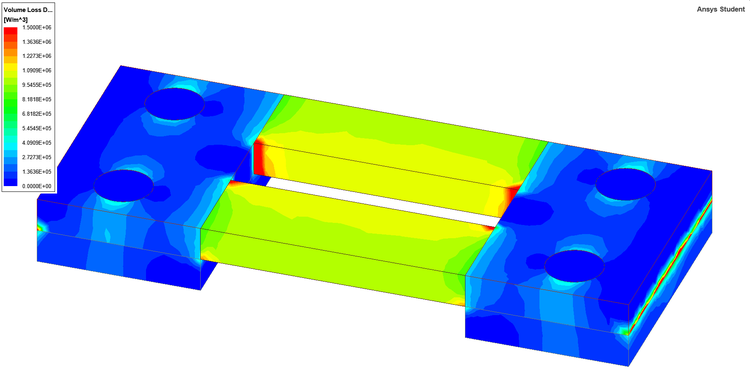
Figure 2. - Possible solution (Left - Maxwell 3D, Right - Q3D Extractor).
Results of the test example. Quantities Voltage drop [mV] Resistance [[math]\text{n}\Omega[/math]] Ohmic loss [W] Maxwell 3D 10.9927 18.3211 6.5956 Q3D Extractor 10.9759 18.2931 6.5855
Ansys Maxwell 3D - Ohmic loss on the surface of shunt resistor. Ansys Q3D Extractor - Ohmic loss on the surface of shunt resistor.
Feladat II. része
In the student version of Ansys EM, Icepak provides an opportunity to study the thermal phenomena of the task. Ansys Icepak is a general CFD solver with specific capabilities for testing the heating and cooling of electronic circuits (PCB / power module).
The task has a natural convection cooling. The excitation is the ohmic loss from the electromagnetic simulation.
Thermal properties of materials. Material Titanium Copper Aluminum Copper-manganin alloy [math]\rho~[\text{kg}/\text{m}^3][/math] 4500 8933 2689 8400 [math]c_{\text{P}}~[\text{J}/(\text{kg}\cdot\text{°C})][/math] 522 385 951 410 [math]\lambda~[\text{W}/(\text{m}\cdot\text{°C})][/math] 21 400 237.5 22 The table below shows the result of the thermal simulation.
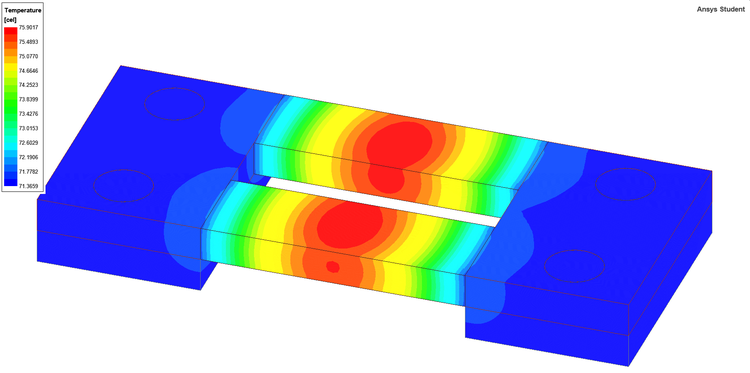
Results of the test example. Quantities Max. temperature [°C] Min. temperature [°C] Max. velocity [m/s] Maxwell 3D + Icepak 75.9284 71.3658 0.2881 Q3D Extractor + Icepak 75.8669 71.3002 0.2880
Ansys Maxwell 3D + Ansys Icepak - Hőmérsékleteloszlás a söntellenállás felületén. Ansys Q3D Extractor + Ansys Icepak - Hőmérsékleteloszlás a söntellenállás felületén. A mintafeladat archivált változatát a következő linken találja: Shunt Resistor (Ansys EM Student 2021 R2).